NLP-Powered Algorithms to Identify Common Data Elements in Operative Notes for Knee Arthroplasty
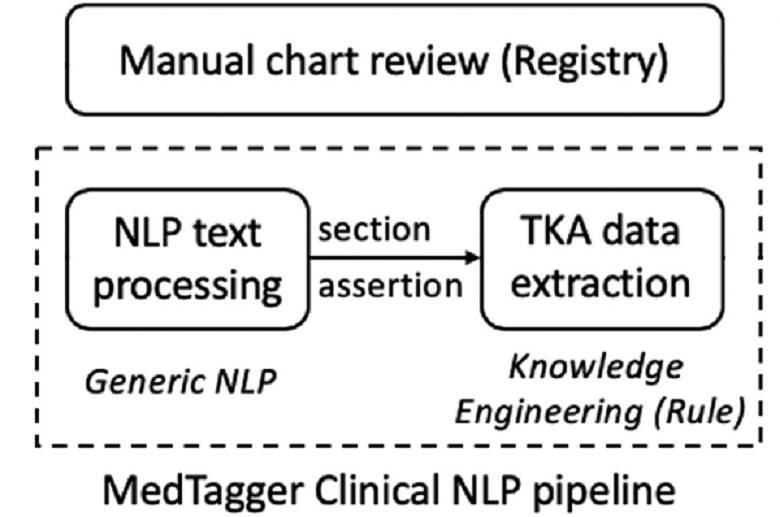
Within a cohort of 20,000 knee arthroplasty operative notes from 2000 to 2017 at a large tertiary institution, we randomly selected independent pairs of training and test sets to develop and evaluate NLP algorithms to detect five major data elements. The size of the training and test datasets were similar and ranged between 420 to 1592 surgeries. Expert rules using keywords in operative notes were used to implement NLP algorithms capturing: (1) category of surgery (total knee arthroplasty, unicompartmental knee arthroplasty, patellofemoral arthroplasty), (2) laterality of surgery, (3) constraint type, (4) presence of patellar resurfacing, and (5) implant model (catalog numbers). We used institutional registry data as our gold standard to evaluate the NLP algorithms. It achieved 98.3%, 99.5%, 99.2%, and 99.4% accuracy on test datasets, respectively. The implant model algorithm achieved an F1-score of 99.9%.